 on Apple Watch" width="696" height="522" />
on Apple Watch" width="696" height="522" /> on Apple Watch" width="696" height="522" />
on Apple Watch" width="696" height="522" />
Apple Watch is a great device for monitoring your health and fitness. With alerts, notifications, and the ECG app, your watch can provide you with important information concerning your heart health.
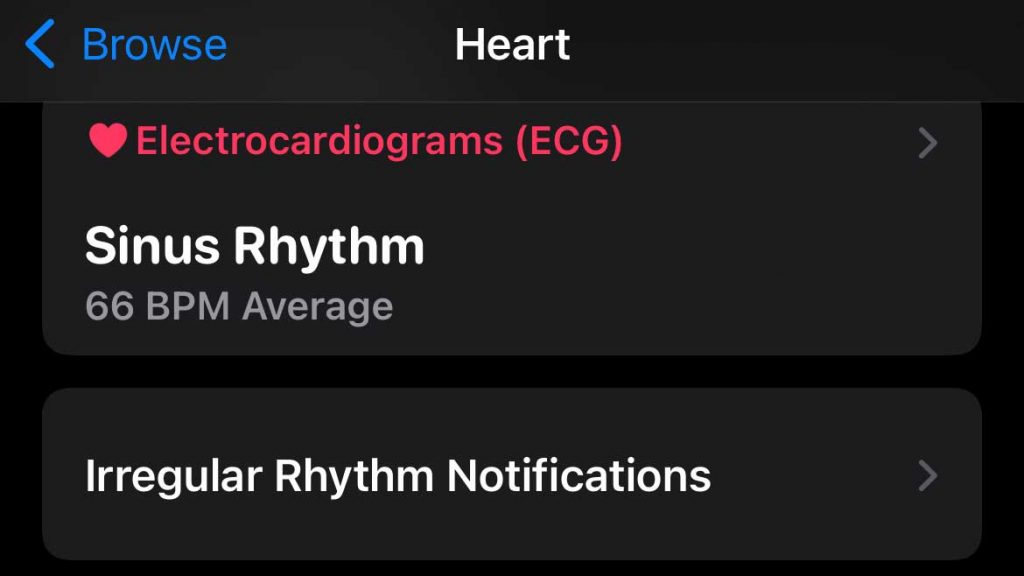
The Apple Watch has two heart rate features that can help to detect irregular heart rate rhythms: the ECG App and the Irregular Rhythm notification feature.
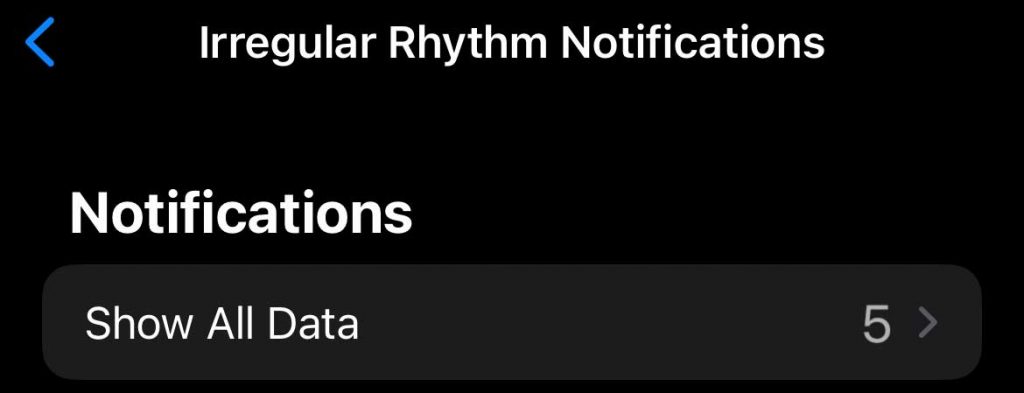
The Irregular Rhythm notification feature checks your heart rhythms and sends a notification if an irregular heart rhythm is detected. This feature is available to all Apple Watch users with a Series 1 or later in over 100 countries!
The ECG app is specific to the Apple Watch Series 4+ models (not SE models or watches in standalone mode) and allows you to perform ECG tests using your Apple watch.
With the ECG app, you can take an ECG recording at any time or follow an irregular heart rhythm notification.
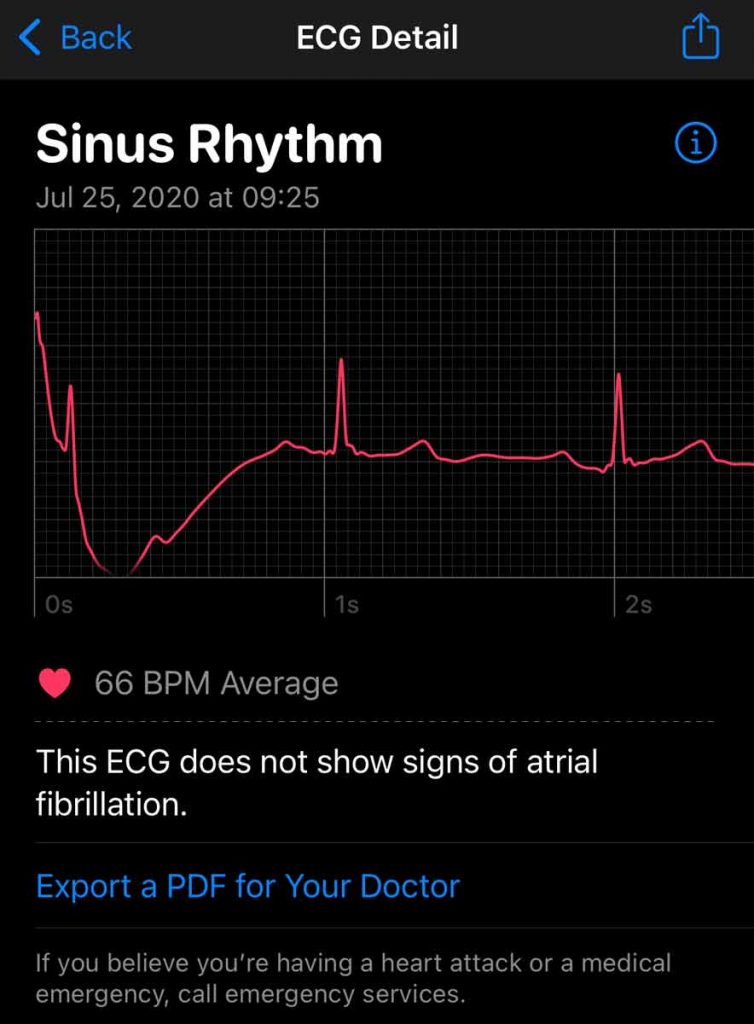
An ECG, short for an electrocardiogram, measures the timings and strength of electrical signals that make up your heartbeat. Your doctor can identify problems in your heart’s rhythm and any irregularities by reading an ECG.

The irregular heart rate feature on the Apple Watch checks for unusually high or low heart rates and uneven heartbeats. Times when your heart is out of its normal and usual rhythm.
You may experience no symptoms or feel like your heart is racing or slowing down, skips a beat, adds a beat, or flutters between beats.
These could be signs of a serious underlying condition like atrial fibrillation (Afib) or another heart issue.
While this feature helps identify irregularities in your heart rate, it is not a diagnostic tool or a substitute for medical care . If you receive a notification, it’s a call to action to further discuss with your doctor or healthcare provider.
If your heart rhythm fluctuates from your norm and your heart beats too fast or slow while sedentary (you appear inactive for 10 minutes), you receive a notification.

The irregular heart rate rhythm notification feature does not constantly look for an irregular heart rate.
Additionally, your Apple Watch only looks for irregular rhythms at rest ; it does not look for abnormalities during exercise. This means the number of readings collected each day and the time between these readings vary depending on how active you are that day.
Because your watch isn’t constantly monitoring your heart rhythm, it cannot detect all instances of irregular heart rhythm.
This feature is also only recommended for users 22 years and older with no prior history of AFib .
The FDA has granted De Novo classification (classified as a low- to moderate-risk device ) for these users.
Before using the irregular notification feature, you need to:
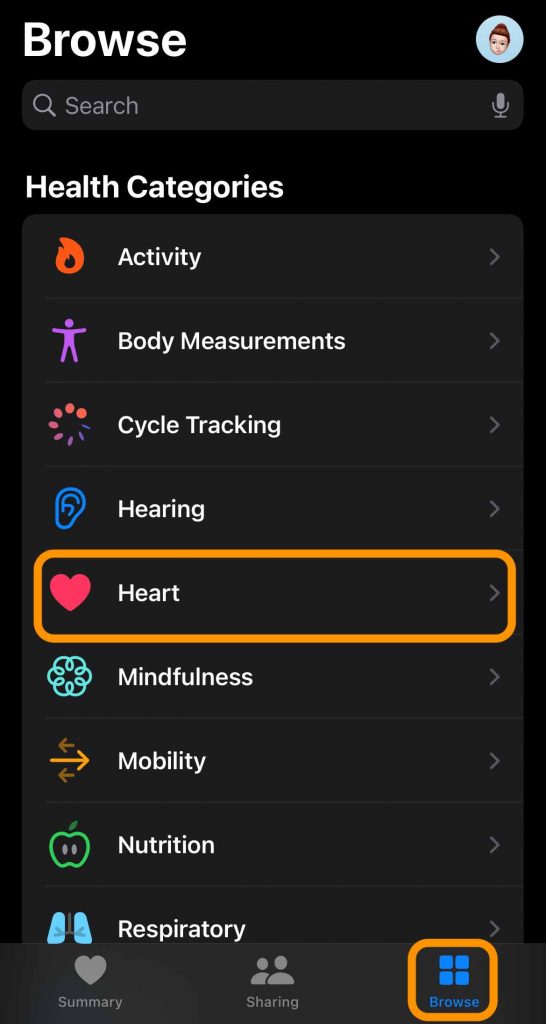
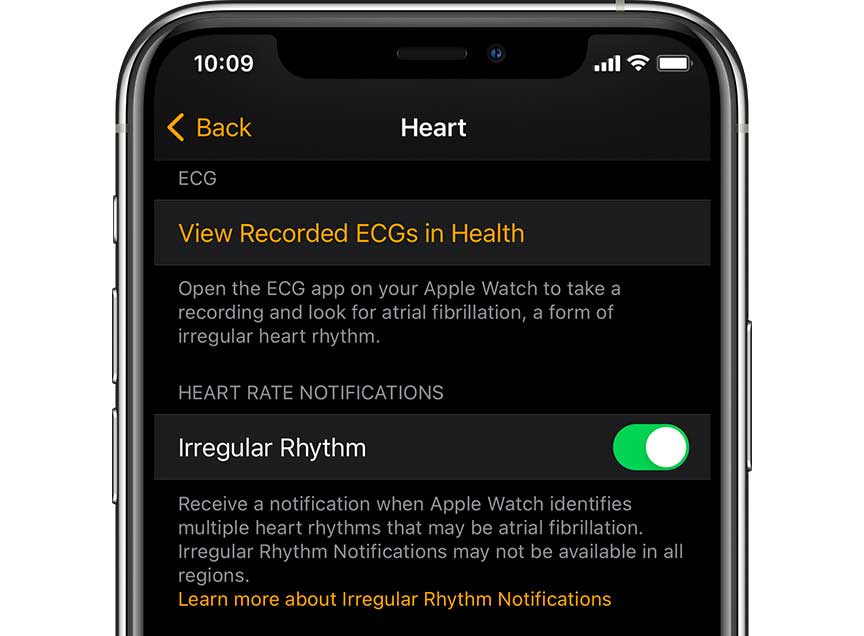
Once you turn on this notfication, you can choose to turn irregular rhythm notifications on or off in the Apple Watch app on your iPhone or your watch in the Settings app.

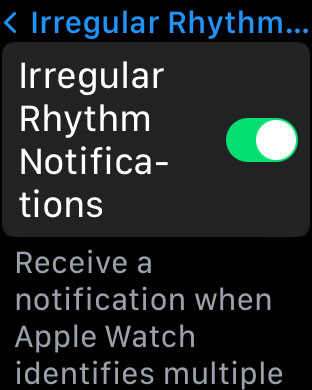 on Apple Watch" width="312" height="390" />
on Apple Watch" width="312" height="390" />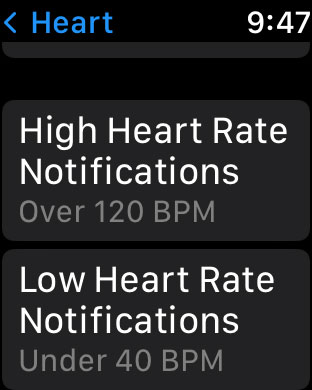 on Apple Watch" width="312" height="390" />
on Apple Watch" width="312" height="390" />View all your heart rate notifications, along with the date, time, and heart rate, in the Health app on your iPhone.
 on Apple Watch" width="720" height="641" />
on Apple Watch" width="720" height="641" /> It can be scary when your Apple Watch sends you irregular rhythm notifications . However, seeing a notification or alert does not automatically mean you have Afib or another heart condition.
Let your doctor or healthcare team know that you have received this notification from your watch and follow it up with them.
If you are experiencing chest pain or a medical emergency, please get in touch with emergency services immediately.
Wearables, like the Apple Watch, play a supportive role in maintaining and managing your health. They are not a substitute for medical care.
You can view a list of the irregular rhythm notifications in the Health app on your iPhone.
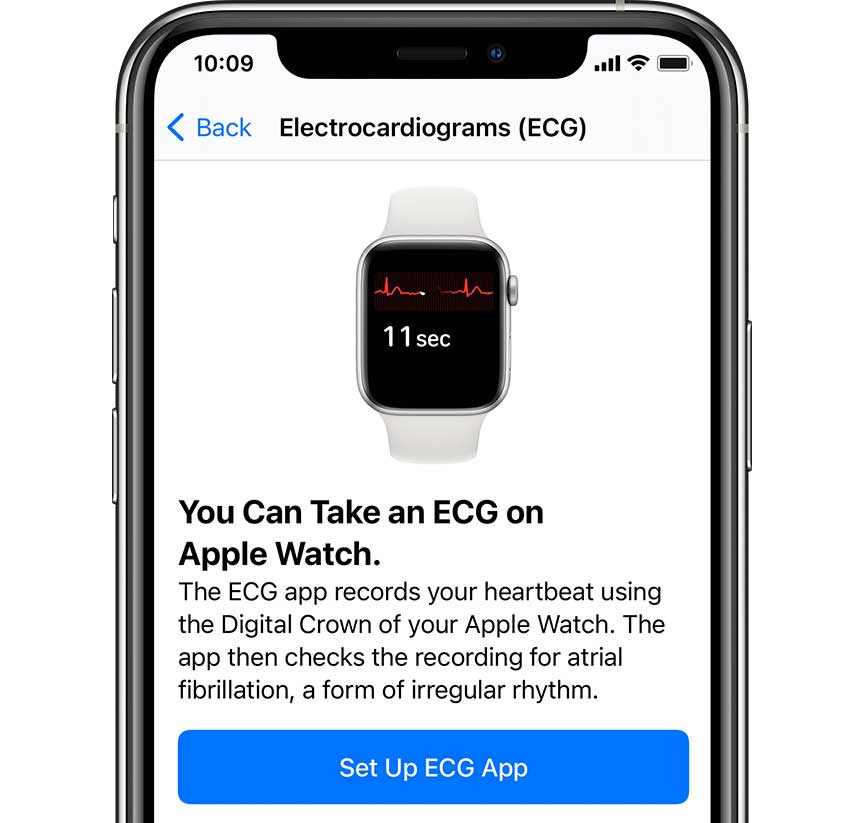
If you receive an irregular heart rhythm notification, it’s a good idea to take an ECG with your Apple Watch to get a closer look.
Not all Apple Watches include this feature–find this app on Series 4 and above, excluding the SE or any Apple Watch set up with family setup.
The ECG app is installed when you first set up the ECG app in the Health app. It’s important to note that the ECG app isn’t available in every country or region–check if it’s available in your region here.
 on Apple Watch" width="864" height="823" />
on Apple Watch" width="864" height="823" />
 on Apple Watch digital crown to get an ECG recording" width="696" height="522" />
on Apple Watch digital crown to get an ECG recording" width="696" height="522" />
After you complete the setup, open the ECG app on your Apple Watch and take an ECG by holding your finger against the watch’s digital crown (you don’t need to push the button.)

If you don’t see the INSTALL button, see this article: Is your Apple Watch ECG App Missing? Here is how to get it back.

You may want to take an ECG if you’re feeling symptoms such as a rapid or skipped heartbeat or when you receive an irregular rhythm notification.
The ECG app records your heartbeat and its rhythm using your watch’s electrical heart sensor.
 on Apple Watch home screen" width="696" height="476" />
on Apple Watch home screen" width="696" height="476" />
 on Apple Watch" width="799" height="398" />
on Apple Watch" width="799" height="398" />If the ECG app isn’t working, take a look at this article: Apple Watch ECG isn’t working? Here’s how to fix it.
You can find the irregular rhythm data and ECG readings in the Health app on your iPhone.
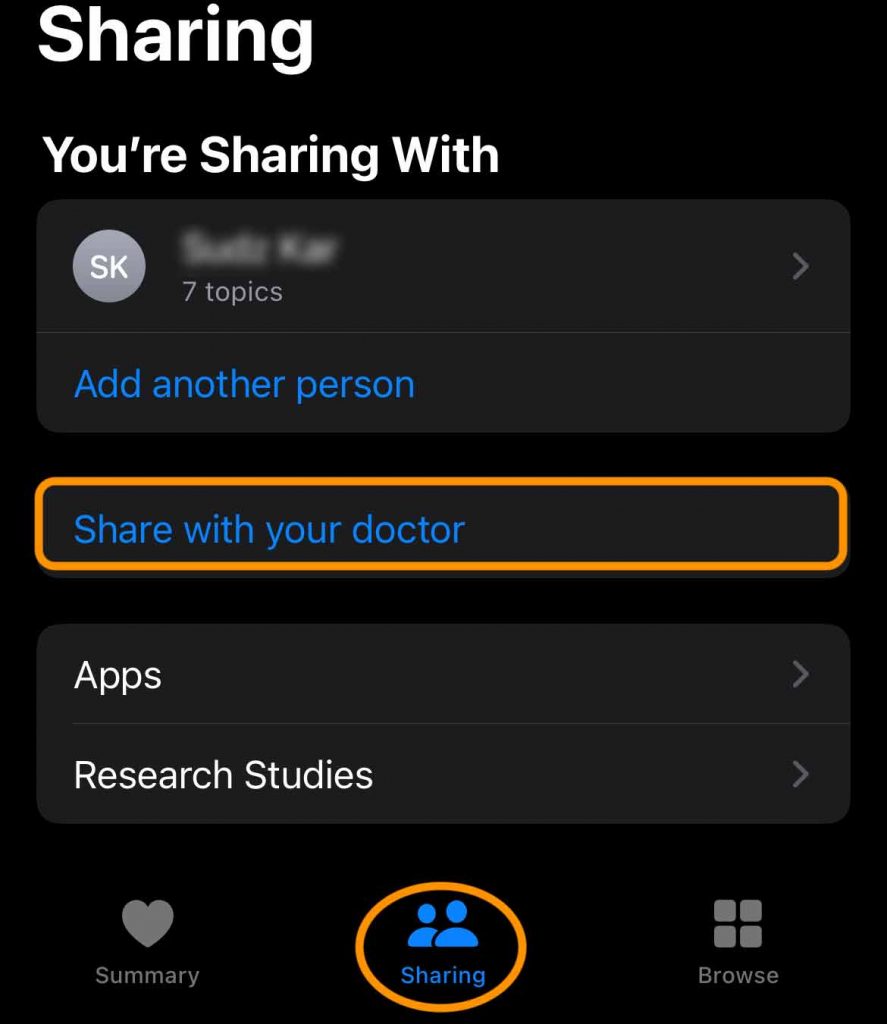
If you’re using iOS 15+, you can also share data with your healthcare provider using the new Sharing tab in Apple Health.
If your doctor or healthcare provider is not part of Apple’s Health Records and Sharing yet, you can still export your health data as a spreadsheet or take screenshots of the particular health data you want to share.
If your heart rate remains above or below a chosen beats per minute (BPM) while you appear to have been inactive for a period of 10 minutes, your Apple Watch can notify you.
These notifications are available only on Apple Watch Series 1 or later for ages 13 and up.
You can turn on heart rate notifications when you first open the Heart Rate app on your Apple Watch or at any time later from your iPhone:
 on Apple Watch" width="720" height="641" />
on Apple Watch" width="720" height="641" />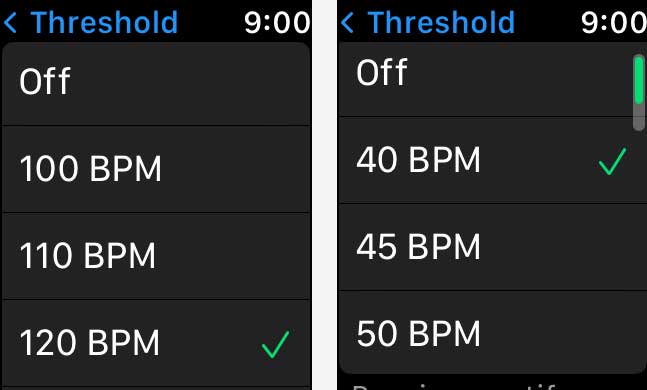 on Apple Watch" width="647" height="390" />
on Apple Watch" width="647" height="390" />Yes, you can turn off the Irregular Rhythm notification without having to turn off notifications for High and Low Heart rates .
Similarly, you can turn off high or low notifications (or both) without impacting irregular heart rhythm.
There is a separate on/off setting for each of these heart rate monitoring features.
The optical heart sensor in Apple Watch uses what is known as photoplethysmography (PPG). Apple Watch uses green LED lights paired with light-sensitive photodiodes to detect the amount of blood flowing through your wrist at any given moment.
By flashing its LED lights hundreds of times per second, Apple Watch can calculate your heart rate. The optical heart sensor supports a range of 30–210 beats per minute.
The optical heart sensor can also use infrared light. This mode is what Apple Watch uses when it measures your heart rate in the background and generates irregular heart rhythm notifications.
PPG signals combined with an algorithm are used to identify an irregular pulse suggestive of Afib ( available with OS 5.1.2 or later, Apple Watch Series 1 and later).
Apple Watch Series 4 and above supports ECG. However, the ECG app is not supported on Apple Watch SE and is disabled on any Apple Watch that doesn’t pair with its own iPhone and is set up via Apple’s family setup.
It uses a PPG-based algorithm and electrical heart sensor that enables the generation and analysis of an ECG when combined with the ECG app.
The ECG app can generate an electrocardiogram (ECG) and classify the rhythm as sinus rhythm (normal rhythm), Afib, high or low heart rate, or inconclusive.
The Apple Heart Study (2017) of 419,297 participants aged over 22 years found a high correlation between irregular pulse-detection on Apple Watch and simultaneous irregular readings recorded with an electrocardiography patch.
Each participant in the study had an Apple Watch (series 1, 2, or 3) and an iPhone. The most recent Apple Watch, which features a built-in ECG, wasn’t part of the study.
In the study Accuracy of Apple Watch for Detection of Atrial Fibrillation by Dhruv et al. (2020) of 50 patients who had undergone cardiac surgery, the overall agreement between Apple watches 4 notification and telemetry was 61%.
The Apple watch series 4 notification correctly identified AF in 34 of 90 instances, giving a sensitivity of 41%, but an inconclusive rhythm was found in 31% of patients.
This study recommends that physicians exercise caution before taking action based on electrocardiographic diagnoses generated by this wrist-worn monitor.
The patients in this study were known to have Afib, and the Apple watch irregular heart rate feature is not recommended for use for people with known Afib.
In 2018, Apple sponsored a two-part, multicenter clinical validation study to validate the ability of the ECG app to generate an ECG waveform similar to a Lead I ECG from a standard 12-Lead ECG and classify heart rhythms as either sinus rhythm or Afib.
Apple tested the app on nearly 600 people, half of whom had atrial fibrillation and half who did not.
When this study group used the watch, the result was inconclusive about 12% of the time.
However, the rest of the time, the app was able to tell people accurately they did not have a-fib 99.6% of the time and accurately told them they did have a-fib 98% of the time, according to the study.
Apple Watch has two optional features that detect irregular heart rhythms: the Irregular Rhythm Notification Feature (available on Apple Watch Series 1 and later) and the ECG app (available on Apple Watch Series 4+).
The Irregular Rhythm Notification Feature opportunistically collects heart rhythm readings in the background and notifies you of the presence of an irregular heart rhythm.
The ECG app allows you to generate an ECG reading whenever you wish and allows you to share the data with your doctor.
Overall, The Apple watch ECG App, and irregular heart rate feature provide acceptable reliability when generating an ECG and identifying Atrial fibrillation and other clinically relevant arrhythmias.
I hope this article has helped you understand and access your Apple watch’s irregular heart rate rhythm feature and ECG App.
If you have any more questions or anything to add, please feel free to let us and everyone else know about it in the comments section down below!
If you liked this article, you could follow us on social media by using the social media buttons!